Working capital is required by the firm for the purpose of purchasing raw materials, payment of wages and other routine expenses, etc. It is required for financing current assets such as cash, marketable securities, debtors and inventories.
Working capital can also be defined as excess of current assets over current liabilities or difference between the inflow and outflow of funds.
Concepts of Working Capital
Working capital concepts are being categorized into two main heads as follows,
- Balance sheet concept and
- Operating cycle (or) circular flow concept.
1. Balance Sheet Concept
The balance sheet concept explains the working capital in two ways as follows,
- Gross working capital and
- Net working capital.
Gross Working Capital
Gross working capital helps in solving the problem of managing individual current assets in two aspects,
(i) A firm must finance only those current assets which are useful and does not result in idle investment and inadequate return on investment in current assets, ultimately increases the risk. If investment made in current assets which are not productive then they block the capital which leads to insufficient capital to meet current obligations of the firm. Hence, firm must maintain only adequate working capital which is required for its business.
(ii) It is necessary for management to secure some amount of funds in order to finance the current assets. Firm must maintain adequate funds to meet additional working capital if business is increased. Financial manager must have knowledge of evaluating the level of current assets required and different sources of financing current assets.
Net Working Capital
The concept of net working capital is useful for management in identifying the permanent sources for financing the working capital requirements. It represents the liquidity position of the firm. Net working capital explains that every firm must have current assets more than current liabilities to meet current obligations effectively. In order to maintain a margin of current assets, it must be device of current liabilities. Quality of current assets implies the structure of current assets. The quality of current assets reflects the liquidity position of the firm. If a firm maintains high level of current assets but if its quality is not appropriate then it may lead to inadequate liquidity position which have impact on solvency of the firm. When current liabilities are more than current assets it leads to negative net working capital which is harmful for the firm.
2. Operating Cycle (or) Circular Flow Concept
The time period needed to convert sales into cash is known as an operating cycle. In a manufacturing company, operating cycle consists of three stages,
- Purchase of resources which are required in a manufacturing company such as raw material, labor, power and fuel etc.
- Manufacturing of the product involves production process is a conversion of raw material into work-in-progress and then transform into finished goods.
- The ultimate stage is, sale of the product which can be in cash or credit. Credit sales usually create account receivable for collection.
Firm must retain liquid assets for purchase of raw materials and payment of expenses like salaries and wages, taxes, operating expenses, etc. Gross operating cycle is the sum of inventory conversion period and debtors conversion period.
The inventory conversion period is the time period required for producing and selling the product.
The debtor’s conversion period is the time period needed to acquire the outstanding amount from customers to whom goods are sold on credit.
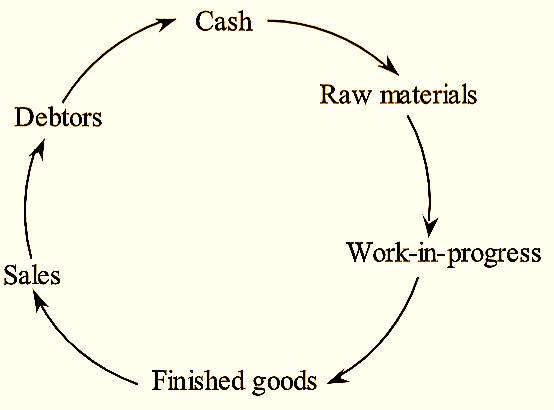
Figure: Operating Cycle.
Gross operating cycle = Inventory conversion period + Debtors conversion period
Net operating cycle = Gross operating cycle – payables deferral period
The need for working capital results in the growth and expansion of business of a firm.
Need for Working Capital
Each and every company needs working capital in order to perform/carry out the day-to-day activities inspective of its size whether small (or) big because without working capital the company would shut down.
Usually, mainly due to the time period taken between production and realization of cash from sales gives rise to the need for working capital wherein, an operating cycle is engaged in raising cash from sales due to time lapse in purchase of raw-materials and production, production and sales and so on.
Therefore, working capital is required due to the following reasons/purposes,
- To purchase the raw-materials, components and spare parts.
- For paying the wages and salaries.
- For meeting daily expenses and overhead costs like fuel, power, office expenses so on.
- For incurring/making selling expenses like packing, advertising so on.
- For enabling, credit facilities to the customers.
- For maintaining the inventories such as raw-material, work in progress, stores and spares and finished stock.
