A Universal Surface Gauge is an essential precision measuring instrument widely used in machining, engineering, and inspection processes. It helps mark accurate reference lines, check surface flatness, and align components with high precision. This instrument plays a crucial role in industries requiring accurate dimensional measurements and layout marking.
What is Universal Surface Gauge?
A Universal Surface Gauge is a mechanical measuring tool designed to scribe fine and precise lines on a workpiece for accurate machining. It consists of a base, scriber, post, rocker arm, and various adjustment mechanisms, enabling it to function efficiently in engineering workshops. The gauge is typically used in conjunction with a surface plate, ensuring high accuracy.
The primary purpose of a Universal Surface Gauge is to transfer precise dimensions, align workpieces, and inspect flatness or parallelism between surfaces. Its adaptability and ease of use make it an indispensable tool in mechanical workshops.
Parts of a Universal Surface Gauge
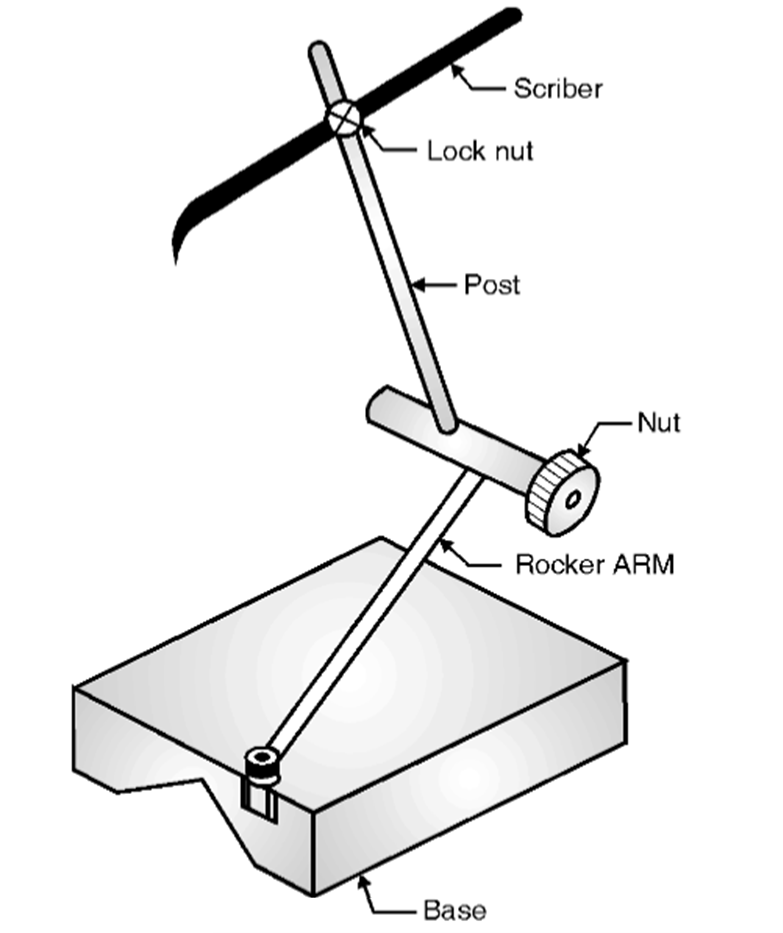
A Universal Surface Gauge consists of several key components that contribute to its functionality. Each part has a specific role in ensuring accurate marking and measurement.
1. Base:
- The base is the heaviest part of the gauge, providing stability.
- Made from hardened steel or cast iron.
- Ensures the instrument remains steady while marking or measuring.
2. Rocker Arm:
- Holds the vertical post in position.
- Enables angular adjustments to mark inclined surfaces.
- Connected to the nut, allowing controlled movement.
3. Post:
- A vertical rod that supports the scriber and other attachments.
- Adjustable in height to mark at different levels.
- Often equipped with a fine adjustment screw for precision.
4. Scriber:
- A pointed tool made from hardened steel.
- Used to mark fine, accurate lines on a workpiece.
- Can be replaced or adjusted for different applications.
5. Lock Nut:
- Secures the scriber in the desired position.
- Prevents movement during marking, ensuring precision.
6. Nut:
- Controls the movement of the rocker arm and post.
- Allows adjustments to achieve the required position.
Additional Features:
- Some advanced models may include magnifiers or dial indicators to enhance accuracy.
- Magnetic bases for securing the gauge on ferrous surfaces.
Construction of a Universal Surface Gauge
The construction of a Universal Surface Gauge follows a rigid and precise design to maintain its accuracy over prolonged use. Here’s how it is constructed:
Material Composition:
- Base: Made from cast iron or tool steel, providing weight and stability.
- Scriber: Hardened steel or tungsten carbide to ensure durability.
- Post & Rocker Arm: Stainless steel or alloy steel for strength and corrosion resistance.
Manufacturing Process:
- Casting the Base: The base is cast and machined to ensure a perfectly flat bottom surface.
- Grinding & Polishing: All metal parts are finely ground and polished to enhance smooth movement.
- Assembly of Parts: The post, scriber, lock nut, and rocker arm are assembled with precise tolerances.
- Quality Testing: The final product undergoes accuracy testing before being approved for industrial use.
The gauge’s reliability depends on precise manufacturing and assembly techniques, ensuring its effectiveness in metrology applications.
Working Principle of a Universal Surface Gauge
The Universal Surface Gauge operates based on a simple yet effective principle. It consists of a scriber mounted on an adjustable arm, which is positioned against a flat surface (like a surface plate or workbench). The user moves the gauge along the surface, allowing the scriber to mark precise lines on the workpiece.
Step-by-Step Working Process:
- Positioning the Base: The base of the surface gauge is placed firmly on the surface plate or workbench to ensure stability.
- Adjusting the Scriber: The scriber is adjusted to the required height using the lock nut and rocker arm.
- Locking the Position: The nut and lock nut ensure that the scriber remains in the desired position for accurate marking.
- Marking the Workpiece: By sliding the base along the surface, the scriber creates a precise marking line on the workpiece.
- Inspection and Adjustment: The markings are checked, and fine adjustments are made as necessary for further machining.
The precision of the Universal Surface Gauge is determined by the accuracy of its parts and the quality of the surface plate used.
Advantages of a Universal Surface Gauge
A Universal Surface Gauge offers several advantages, making it a preferred tool for machinists and engineers.
- High Accuracy: Provides precise markings for machining and inspection. Used with surface plates to ensure accuracy in measurements.
- Versatile Applications: Can be used for marking, measuring, and alignment. Works with both small and large workpieces.
- Durability & Longevity: Made from high-quality materials for extended use. Resistant to wear and tear.
- Easy to Use: It Simple construction makes it user-friendly. It Requires minimal training to operate effectively.
- Cost-Effective: It Provides high precision at a reasonable cost. It Reduces errors, saving time and resources in machining processes.
Applications of a Universal Surface Gauge
The Universal Surface Gauge is used in various industries where precise measurement and marking are required. Some common applications include:
- Machining & Fabrication: Marking reference lines on metal, wood, or plastic workpieces. Checking and aligning machine tool components.
- Quality Inspection & Metrology: Measuring the flatness and parallelism of surfaces. Ensuring components meet dimensional tolerances.
- Tool & Die Making: Used in die and mold manufacturing for precision alignment.
- Engineering & Prototyping: Creating accurate layout markings for prototype development.
- Automobile & Aerospace Industries: Used for inspecting critical components requiring high precision.
Disadvantages of a Universal Surface Gauge
Despite its numerous benefits, a Universal Surface Gauge has some limitations.
- Requires a Flat Surface Plate: Accuracy depends on the quality of the surface plate. Any imperfections in the surface can affect precision.
- Manual Operation: Relies on human accuracy and control. Operator error can lead to inaccurate markings.
- Limited to Simple Marking Tasks: Not suitable for complex geometrical measurements. Cannot measure internal features of components.
- Not Suitable for Soft Materials: Scriber may damage or deform soft materials like rubber or thin plastics.
Conclusion
A Universal Surface Gauge is a crucial tool in machining, metrology, and precision engineering. Its ability to provide accurate markings and measurements makes it invaluable in workshops and manufacturing industries. Despite minor limitations, its advantages far outweigh its drawbacks, making it a staple in precision measurement.
