A product has five levels and every level adds some attribute to the basic level which provides value to the consumer. These levels together forms a customer value hierarchy.
Levels of Product
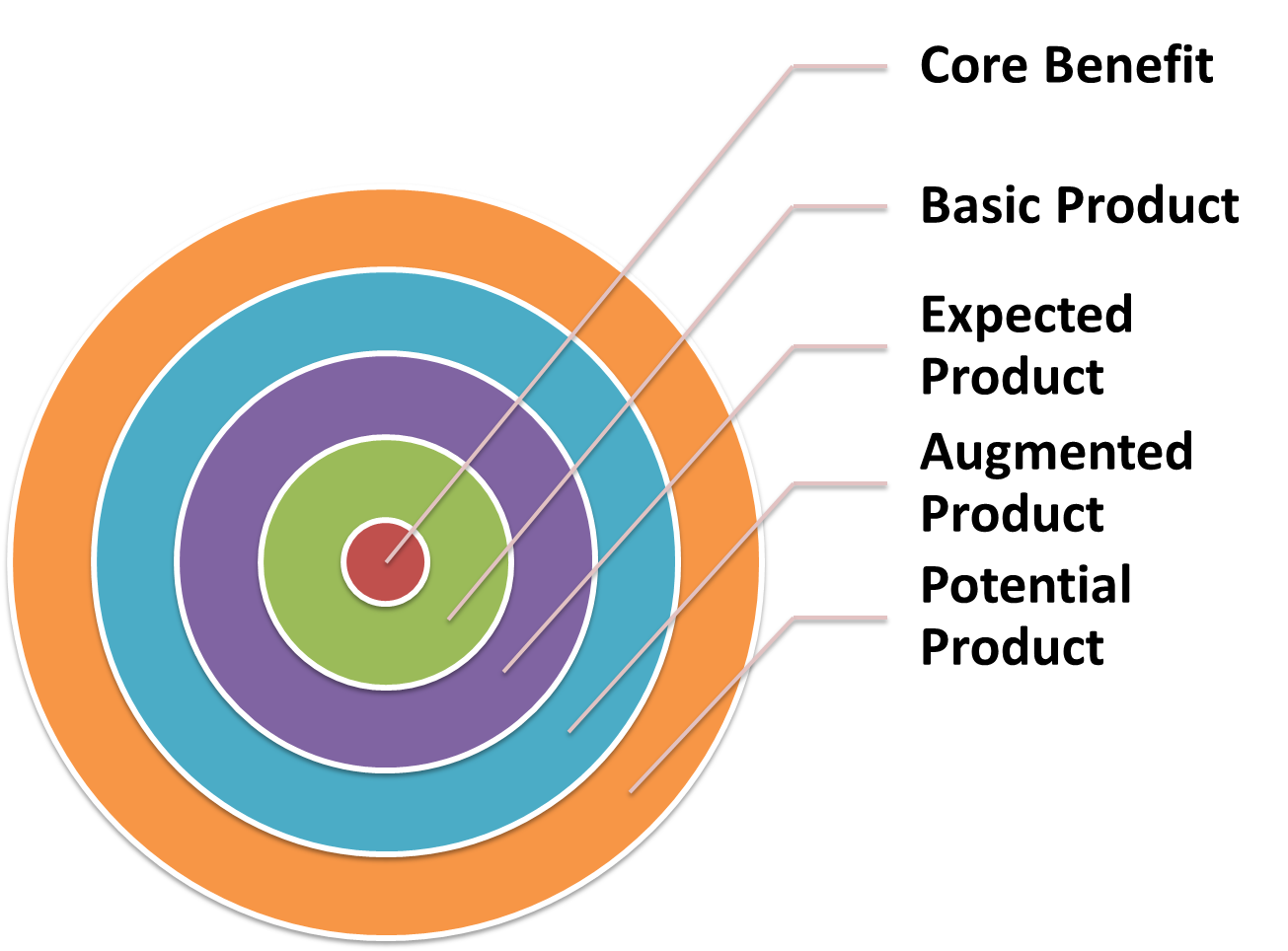
1. Core Benefit
Core Benefit is the most important level of product. Core Benefit is the benefit in which the purchaser of the product derives by purchasing. It helps in satisfying the basic need of a consumer.
Example
The hotel provides rooms for rest. Here, the basic need of customers is rest and sleep. Another example of a customer who buys pen for writing which is his basic need.
2. Basic Product
This is the second level in customer-value hierarchy in which the marketer transforms the core benefit into a basic product by adding some attributes to the product.
Example
A lodge which provides a room to the customers for rest and sleep can add some attributes to the room like an attached washroom, dressing table, a basic bed, a closet for keeping clothes etc.
3. Expected Product
This is the third level in the customer value hierarchy in which the marketer develops an expected product. The consumers normally expect the product to have some attributes before purchasing it. These are the common expectations of the purchaser of the product Every marketer tries to meet the expectations of the consumers, so that the consumers get satisfied after the purchase of the product.
Example
The purchaser of a four wheeler automobile expects the showroom to have a well designed interiors and a good handling experience.
4. Augmented Product
This is the fourth level of the product in which the marketer develops an augmented product which is beyond the expectations of the consumers. In the developed countries like USA, UK and Australia, brands compete in this level. Every firm determines the expectations of consumers and manufacturers the products beyond their expectations.
5. Potential Product
This is the last level in customer-value hierarchy which includes all the expected expansions and transformations that a product may undergo in the future. This is the final level and no more additional features can be added to the product In this level, the marketers determine new ways to satisfy buyers and differentiate their product.
