A product is defined as an offering made by the company in the market for satisfying the needs and wants of the consumers. A tangible product consists of watches, pens, tables, chairs, automobiles etc., and intangible services consists of doctor’s service, insurance, health care benefits etc.
Types of Product
The products are classified into many different types which are as follows,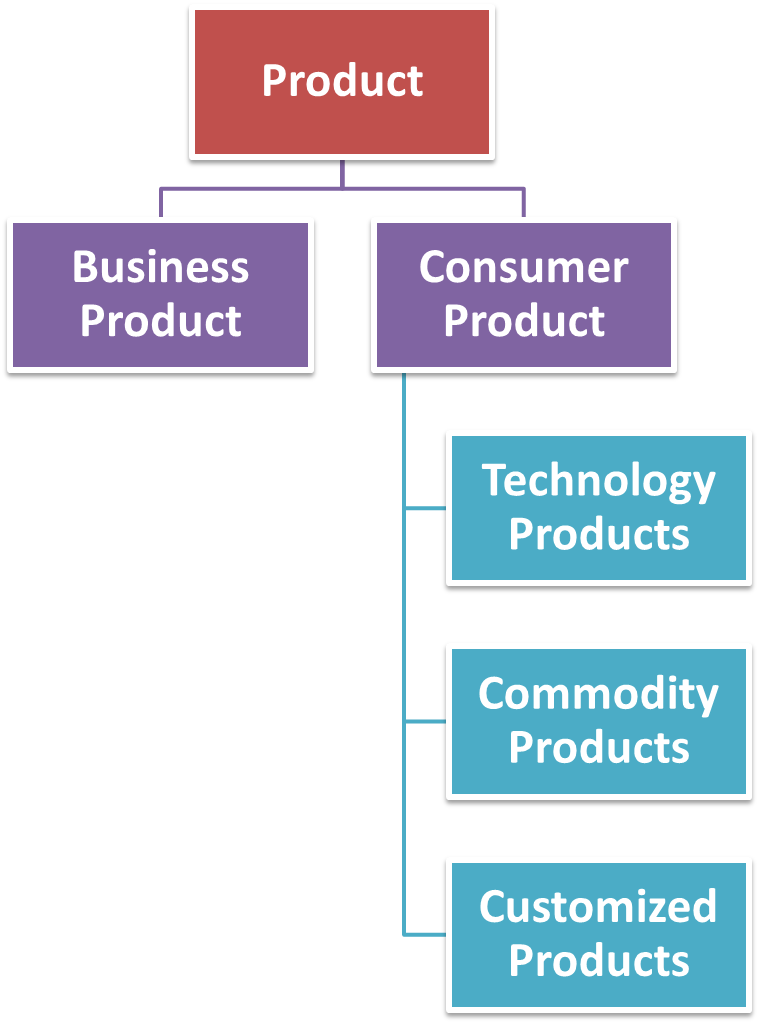
1. Business Product
On the basis of the intentions or aims of customers, the products may be classified as Business Product, or Consumer Products. The difference between these two products exist with regard to their usages. The Business Products are usually used for producing goods or services for making the operations of the organization effective or for the purpose of resale to other customers.
2. Consumer Product
The consumer products are purchased for fulfilling the personal needs and wants of the individual. In some situations, the same product is classified as a consumer product or business product based on their expected use.
The consumer products are classified on the basis of the level of effort spent for purchasing them. The products that are purchased regularly, have the low unit price and requires less effort by the consumers for purchasing them. The products that are not purchased regularly have high unit price, and requires significant efforts by the consumers for purchasing them. The various types of consumer products are as follows,
(i) Technology Products
The technology products have many inconsistencies which might either delay or stop the customers from adopting it. The firms must handle these issues carefully so as to make the customers feel comfortable.
The products are developed with the help of increasing technology. A restless or uneasy relationship exists between customers and technology which influences the way they purchase and use the technological products. There are many inconsistencies which regulates the relationship between technology and customers.
(ii) Commodity Products
It is very difficult to distinguish the commodity products. If the risks associated with these products are minimized, then it can help the suppliers in their products differentiation and they can charge a premium from the consumers.
The marketers also find it difficult to sell such products. So, for selling these product easily, the firms adopt the strategy of price cutting. Traditional marketing approaches such as bundling products strategies or providing value improving services like training and consulting helps in differentiating the commodity. But these strategies will be very costly for the firm and makes it difficult for them to recover.
The suppliers who minimize the risk of such commodities, are usually paid a premium by the customers. The firms can divide their customers in segments according to their tolerance and exposure to risk and thereby provide risk- reduction packages to them for price.
(iii) Customized Products
The tools of database management help the firms in designing or creating customized products for the customers and establish a learning relationship with them. A firm must consider the following factors while designing the customized products,
- The firms should know that customers do not want more choices.
- In segmented marketing, the firm creates an average product as it can be liked by many customers.
- A firm should build a learning relationship with the customers.
- Modular designs can be used for customization
- Customization must be used for digital products as it can be used easily and is less costly.
