A pneumatic load cell is a force-measuring device that uses compressed air or gas pressure to determine the applied load. It operates based on the principle of balancing an applied force using air pressure and is commonly used in precision weighing applications where high accuracy and environmental resistance are required.
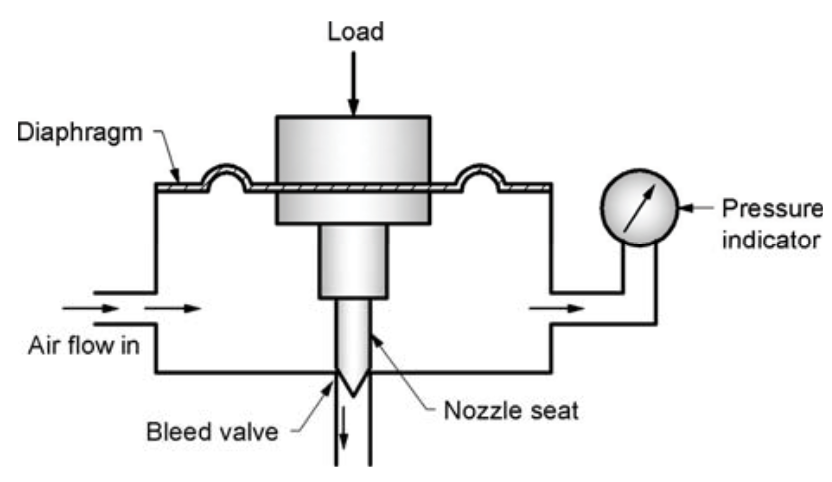
Construction of Pneumatic Load Cell
The key components of a pneumatic load cell include:
- Loading Platform: The surface where the force is applied.
- Diaphragm: A flexible membrane that deforms when a load is applied.
- Nozzle and Nozzle Seat: A mechanism to control airflow and create pressure balance.
- Bleed Valve: Allows controlled air escape to maintain a steady pressure.
- Pressure Indicator (Gauge): Measures the pressure change corresponding to the applied load.
- Air Supply System: Provides a steady flow of compressed air.
- Sealed Chamber: Houses the diaphragm and air system to ensure pressure integrity.
Working Principle of Pneumatic Load Cell
The pneumatic load cell functions by balancing an applied force using air pressure. The working mechanism involves:
- Load Application: A force is applied to the loading platform.
- Diaphragm Deformation: The force causes the diaphragm to flex downward.
- Air Flow Adjustment: Air enters the chamber and flows through the nozzle.
- Pressure Balancing: The bleed valve releases air, maintaining a steady pressure inside the chamber.
- Measurement via Pressure Indicator: The pressure required to balance the diaphragm deformation is measured and converted into a force or weight reading.
The system reaches equilibrium when the force exerted by the air pressure balances the applied load, making it highly accurate for precision measurements.
Advantages of Pneumatic Load Cell
The pneumatic load cell offers several key benefits:
- High Precision: Provides highly accurate force measurement.
- No Electrical Components: Eliminates issues related to electrical noise and interference.
- Explosion-Proof Design: Suitable for hazardous environments (chemical plants, refineries, etc.).
- Temperature and Humidity Resistant: Less affected by temperature fluctuations compared to strain gauge-based load cells.
- No Fluid Leakage Issues: Unlike hydraulic load cells, pneumatic load cells do not require liquid, preventing leakage problems.
- Overload Protection: The air pressure system prevents damage from sudden overloads.
Disadvantages of Pneumatic Load Cell
Despite its advantages, the pneumatic load cell has some limitations:
- Slower Response Time: Due to the time required for air pressure balancing.
- Requires Constant Air Supply: Needs a continuous and stable compressed air source.
- Limited Load Capacity: Typically used for low-to-medium force measurements.
- Higher Maintenance: Regular calibration is needed to maintain accuracy.
Applications of Pneumatic Load Cell
Pneumatic load cells are widely used in industries where precise and stable force measurement is required:
- Precision Weighing: Used in laboratory and industrial weight measurements.
- Food and Pharmaceutical Industries: Suitable for hygienic applications as they are clean and fluid-free.
- Chemical and Explosive Environments: Preferred due to their explosion-proof nature.
- Aerospace and Automotive Testing: Used for component testing and calibration.
- Manufacturing Industry: Ensures correct force application in production processes.
- Medical Equipment Calibration: Used for high-precision force measurements in medical devices.
Conclusion
The Pneumatic Load Cell is a precise and reliable force-measuring instrument, ideal for environments requiring explosion-proof and interference-free operation. It utilizes air pressure to balance an applied force, ensuring accuracy and stability. While it requires a constant air supply and has a slower response time, its applications in industries like pharmaceuticals, aerospace, and hazardous material handling make it a valuable tool in precision force measurement.
