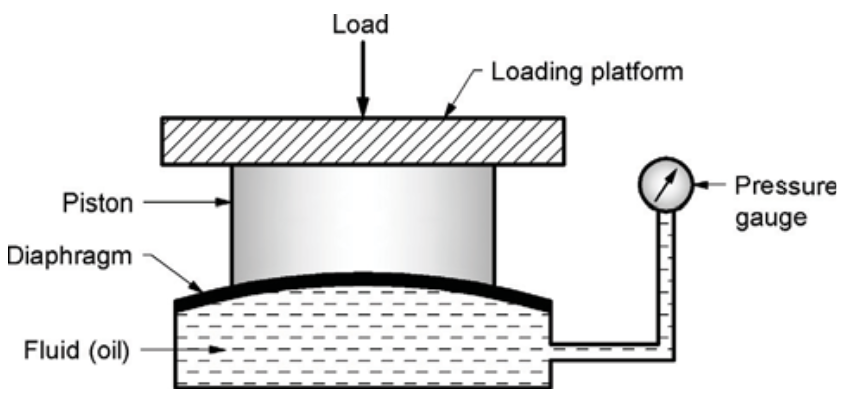
A hydraulic load cell is a force-measuring device that uses hydraulic pressure to determine the applied load. It operates based on Pascal’s principle, where an external force applied to a fluid-filled chamber results in a pressure change that can be measured using a pressure gauge. Hydraulic load cells are commonly used in industrial applications requiring precise force measurement.
Construction of Hydraulic Load Cell
The main components of a hydraulic load cell include:
- Loading Platform: A rigid structure that receives the applied load.
- Piston: Transfers the force from the loading platform to the hydraulic fluid.
- Diaphragm: A flexible membrane that separates the fluid chamber and transmits pressure changes.
- Hydraulic Fluid (Oil): A non-compressible fluid that transmits the force inside the system.
- Pressure Gauge: Measures the pressure inside the hydraulic chamber, which corresponds to the applied load.
- Sealed Chamber: Encloses the hydraulic fluid to ensure accurate force transmission.
Working Principle of Hydraulic Load Cell
The hydraulic load cell operates based on Pascal’s Law, which states that a pressure change in an incompressible fluid is uniformly distributed in all directions. The working mechanism involves:
- Load Application: A force is applied to the loading platform, which transfers it to the piston.
- Force Transmission: The piston moves downward, compressing the hydraulic fluid.
- Pressure Increase: The applied force increases the fluid pressure inside the chamber.
- Measurement via Pressure Gauge: The pressure gauge converts the hydraulic pressure into a readable value.
- Calibration and Output: The gauge is calibrated to display the force or weight in appropriate units.
Advantages of Hydraulic Load Cell
The hydraulic load cell offers several benefits:
- High Durability: No electrical components, making it resistant to environmental conditions.
- No Power Requirement: Operates purely on hydraulic principles.
- Accurate Measurement: Provides reliable force readings with minimal drift.
- Wide Range of Applications: Used in harsh industrial environments.
- Insensitive to Temperature Variations: Less affected by thermal fluctuations.
- Overload Protection: Can handle high-force applications without significant damage.
Disadvantages of Hydraulic Load Cell
Despite its advantages, the hydraulic load cell has some limitations:
- Potential Fluid Leakage: Requires proper sealing to prevent hydraulic fluid loss.
- Maintenance Requirements: Needs periodic fluid replacement and system checks.
- Limited Dynamic Response: Slower reaction time compared to electronic load cells.
- Bulkier Design: Larger size compared to strain gauge-based load cells.
Applications of Hydraulic Load Cell
Hydraulic load cells are widely used in various industries, including:
- Weighing Systems: Used in truck scales, industrial weighing, and platform scales.
- Material Testing: Determines the force applied in tensile and compression testing.
- Aerospace Industry: Measures forces in aircraft testing and component evaluation.
- Construction Industry: Used in bridge and structural load monitoring.
- Manufacturing: Ensures correct force application in industrial processes.
- Mining and Heavy Equipment: Measures loads in cranes, excavators, and lifting systems.
Conclusion
The Hydraulic Load Cell is a robust and reliable force-measuring device suitable for various industrial applications. It leverages Pascal’s Law to measure force based on hydraulic pressure, offering advantages like durability, accuracy, and no power dependency. While it requires maintenance and has potential fluid leakage issues, its applications in weighing, material testing, and structural monitoring make it an essential tool in many engineering fields.