Steps for Preparing Project Report
Selecting and Defining Topic
Project topic has to be selected with respect to the plan of the research being undertaken and preferably the area of specialization selected by the researcher. While taking into consideration a topic, one need’s to discuss and self interrogate if it sparks an interest. Discussing ideas may help refine focus. Going through former projects of experienced people, skimming through the titles of research papers over the past years, and reading the abstracts would prove useful.
Dissertations of earlier project topic can offer inspiration and useful suggestions for further research. An associated topic of interest, that one is already involved in and something that fits with the theory or methodology one has been working with.
Project topic should be selected in consultation with the other member’s views and should be communicated to the organisation. Preferences for particular kinds of research topic should be studied. Discussing the proposed topic is appropriate. The topic selected should be realistic and practical to be accessible to equipment and to the population of interest.
Writing chapters
A project report is a very important feature of a project. It should be properly structured, so that necessary and appropriate information regarding the project is included. The aim of the project is to produce a good report. As and when the various stages of a project is completed, design document has to be progressively converted to a project report. A tidy, well layout and consistently formatted manuscript makes for easier reading and is indicative quantity does not produce quality. Conciseness, clarity, and elegance are valuable qualities in report writing.
A report, which is written for the sake of being written, has very little value. The most important thing to be kept in mind right through the report writing process is that a report is written to be read by someone else. The project report should be written with great care as someone else can carry on working and improving on it. This is the central goal of report-writing. Before writing a report, the intended audience should be considered. In short, care should be taken that the report is of publishable quality and that it is readable and useful in general.
Following are the various chapters for research paper writing:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
- Results and discussion
- Conclusion
Chapter 1: Introduction
In order to start the chapter with a good introduction the following questions should be answered. A project should consist of following questions as this could be the basis for introduction. It should be remembered that it’s the introduction to the project and not an introduction to the topic of the project.
- What was the purpose of the project report?
- How was the topic chosen?
- What were the main aims and objectives of the project report?
- What is the scope of the research project? (If your dissertation/project is focused on one particular group, industry or technology you might include introductory remarks here.)
- What were the limitations of the work?
- How is the text arranged in the dissertation/project?
- Is there anything particular to note that will make it easier for the person reading your dissertation/project to follow the work (e.g. about the format of referencing, layout of charts/tables)?
Chapter 2: Literature review
- An introductory paragraph which explains what is discussed in the chapter and why it is necessary to include this as part of the project.
- Demonstration of the literature search.
- Demonstration of a well read matter up to date material.
- Summarising the literature.
- Highlight trends in the discussion of the topic, for example over time, by geography, by sector.
- Commenting on the value of what is read.
- Organizing the findings of the literature review to fit in with the main themes of the research project.
- Identifying gaps or anomalies in the literature.
- Demonstration of what is assimilated, understood, read, written.
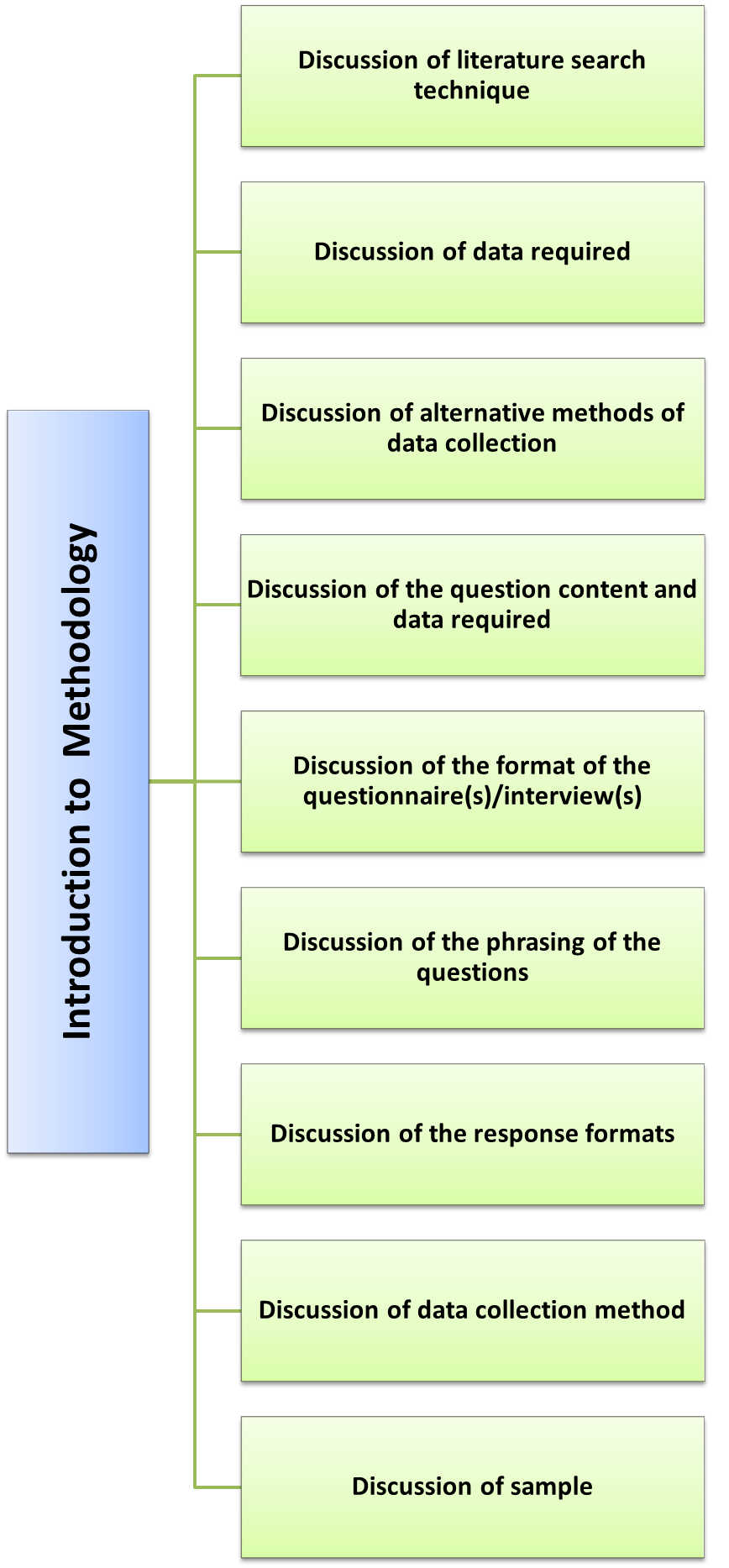
Chapter 3: Methodology
The methodology chapter is used to justify the choice of methods employed during the research project. Various options for conducting a research are demonstrated. Although much of the methodology chapter focuses on data collection, it is also worth acknowledging that the techniques used for the other activities related to the research project: literature searching, sampling or case study selection, data analysis.
Introduction to Chapter 3
- What does this chapter discuss?
- Why is it necessary to include this discussion in the project?
Chapter 4: Results and discussion
- An introductory paragraph which explains what is discussed in the chapter.
- Discussing results with reference to the findings of the literature review. The degree of repetition can be minimized by good cross referencing. The reader expects an interrelation between the results and what was established in the literature review.
- Writing thematically. In majority of cases, this means following a structure determined by the arrangement of themes in the literature review. It is not very sophisticated to take each questionnaire question and summarize the results. The questionnaire should be designed for the surveyed population to answer the questions and not designed to provide only with a thematic framework.
- Add value to the results comments.
- Highlight and provide analysis of any new themes that have emerged from the research.
- Recommendations.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
This should be a conclusion to the whole project (and not just the research findings). Check that the research answers the following questions
- Did the research project meet its aims (check back to introduction for stated aims)?
- What are the main findings of the research?
- Are there any recommendations?
- Do you have any conclusions on the research process itself?
- Where should further research be focused?
Subject Matter
This step is primarily concerned with the development of a subject. There are two ways in which to develop a subject
- Logically
- Chronologically
Deciding the style and structure
A project report has to be a scholarly effort, which results in a contribution to the literature, either as a new theory, a new application of an existing theory or practice or a synthesis of the literature. As such, the report should include a significant literature review, research questions/hypothesis, appropriate research methodology, findings, and conclusions.
As the project topic is selected, the writing subject matter and the structure are decided. After this, the reference style of presenting the project report is also considered. There are various styles of reference used, while writing a project report, some of which are discussed in the later part of this chapter.
Structure of Project Report
The structure of project report consists of:
Title page: The title page should include
- Title of report
- Name of the Company
- Who prepared it?
- Nature and Date of submission
Certificate from faculty guide
Certificate from the director
Certificate from the company
Declaration from Author/Researcher
Acknowledgment: A brief thank you note to the people who have helped you in the project.
Table of Contents: List of various topics covered in the project along with the page numbers as
- Systematically numbered sections and subsections.
- List of tables and figures.
Executive summary: A one-page abstract of the entire report may be all that a busy business executive reads. It should
- Explain the terms of reference, the purpose and scope of the report.
- State the key methods and approach used.
- List the main conclusions.
- List the key recommendations.
Main text of the report
The main text of reports consists of:
Introduction and theoretical background of the study: Often a detailed analysis of the current situation or problem.
Research methodology: Research methodology should include
- Objectives of the research and the operationalization of the key variables.
- The population of case studies and the sampling procedures or selecting cases.
- Data capture instruments used.
- Data collection methods.
- Specific research techniques and applications.
- Data analysis procedures.
- Limitations of the study.
Company Profile: Profile of industry/company/product. It should also cover the profile of industry and the products concerned. This chapter should give a brief background of the company in which the study was conducted and shouldn’t exceed 5 pages.
Analysis and interpretation of Data
Finding and conclusions: It is the heart of the project and should be related to the objectives established.
Suggestions and recommendations: This would be the researcher’s/authors views/opinions on the project. He can give comments but they should be justified and logical.
Appendices: This includes:
- Any explanatory notes that would clutter up the main report.
- Tabulations and calculations not included in the text
- References.
- Copies of questionnaire or visual materials used.
- Bibliography: List of books, magazines, journals, websites, etc. referred.
