A Hartnell Governor is a type of centrifugal governor that uses a spring-loaded mechanism to control the speed of an engine by adjusting the fuel supply. Unlike conventional Watt or Proell governors, which rely solely on centrifugal force, the Hartnell Governor uses a spring to improve stability and responsiveness.
It is classified as a spring-loaded governor and is widely used in high-speed engines due to its fast response, compact design, and improved speed regulation.
Parts of Hartnell Governor
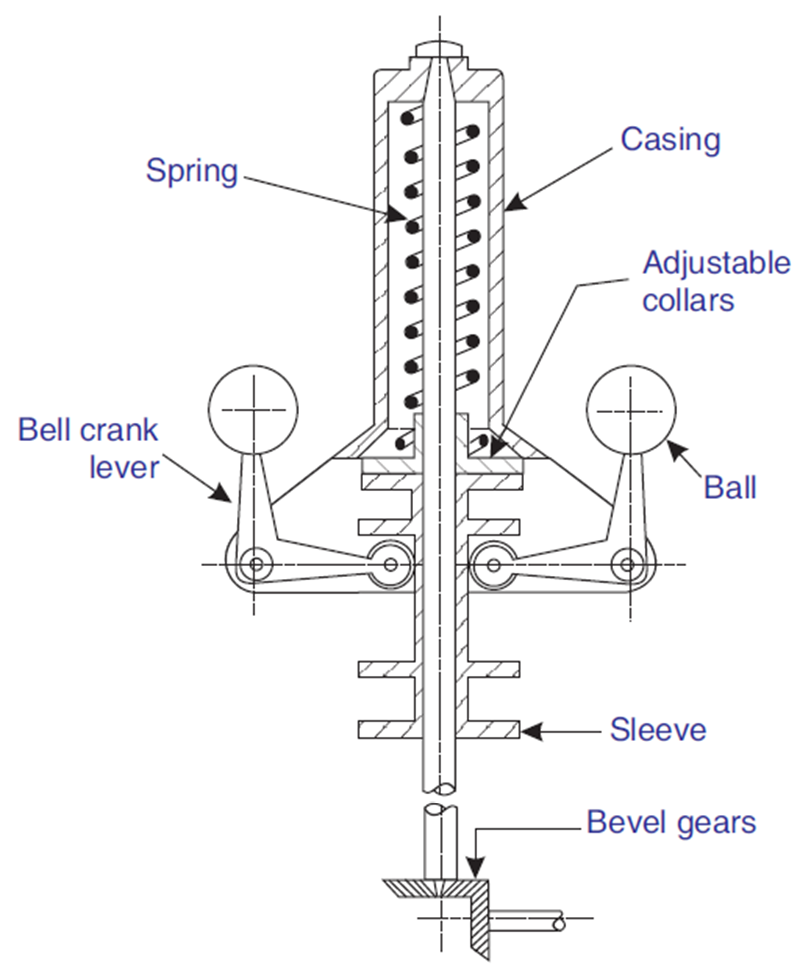
The Hartnell Governor consists of several essential components:
1. Balls (Masses)
- Two metallic balls rotate with the spindle.
- They experience centrifugal force, which moves them outward/inward.
2. Bell Crank Lever
- A pivoted lever that connects the balls to the sleeve.
- Transfers motion from the balls to the throttle valve.
3. Spring
- A helical compression spring placed inside a casing.
- Provides a controlling force to oppose centrifugal force.
- The stiffness of the spring determines governor sensitivity.
4. Adjustable Collars
- Located inside the casing to adjust spring tension.
- Helps in setting the desired engine speed range.
5. Sleeve
- A movable sleeve that slides along the spindle.
- Its movement regulates the throttle valve, controlling fuel supply.
6. Spindle (Vertical Shaft)
- A rotating shaft connected to the engine via bevel gears.
- It carries all moving parts and rotates at engine speed.
7. Casing
- A protective housing for the spring and adjustment mechanism.
8. Bevel Gears
- Transfers motion from the engine shaft to the governor spindle.
- Ensures the governor’s speed is proportional to engine speed.
9. Throttle Valve
- Connected to the sleeve through a lever mechanism.
- Controls the fuel supply based on sleeve movement.
Working Principle of Hartnell Governor
The Hartnell Governor works by utilizing:
- Centrifugal force (generated by rotating balls).
- Spring force (applied through an adjustable spring mechanism).
Step-by-Step Working Mechanism
- Normal Speed Condition: The balls rotate at a constant speed, keeping the sleeve in a stable position. The spring force balances the centrifugal force.
- Increase in Engine Speed: If the engine speed increases, the centrifugal force on the balls increases. The balls move outward, pushing the bell crank lever. This raises the sleeve, compressing the spring. The movement of the sleeve reduces the throttle valve opening, decreasing fuel supply. The engine speed decreases back to normal.
- Decrease in Engine Speed: If the engine speed decreases, the centrifugal force decreases. The balls move inward, allowing the spring to expand. The bell crank lever lowers the sleeve. This increases the throttle valve opening, supplying more fuel. The engine speed increases back to normal.
By balancing centrifugal and spring forces, the Hartnell Governor ensures precise speed control.
Advantages of Hartnell Governor
The Hartnell Governor offers several benefits over conventional governors:
- Faster Response Time: The spring-loaded mechanism ensures quick reaction to speed changes.
- Higher Stability: Unlike traditional governors, the Hartnell Governor is less affected by load fluctuations.
- Suitable for High-Speed Engines: The Hartnell Governor is effective for high-speed engines, unlike Watt or Proell Governors.
- Compact Design: The use of a spring instead of gravity allows a more compact and lightweight design.
- Adjustable Sensitivity: The spring tension can be adjusted using collars, allowing fine control over governor performance.
- No Hunting: Hunting (continuous oscillations) is reduced due to spring damping.
- Increased Fuel Efficiency: Helps in better fuel regulation, optimizing engine performance.
Applications of Hartnell Governor
The Hartnell Governor is widely used in high-speed mechanical and industrial applications:
- Steam Turbines: Used in high-speed steam turbines to regulate speed efficiently.
- Internal Combustion (IC) Engines: Commonly found in automobile and industrial IC engines.
- Power Plants: Helps in maintaining constant generator speed in power plants.
- Marine Engines: Used in marine propulsion systems for speed control.
- Manufacturing and Textile Machines: Ensures uniform speed in textile and industrial machines.
- Hydraulic and Pneumatic Systems: Used in fluid power systems to control motor speed.
Disadvantages of Hartnell Governor
Despite its advantages, the Hartnell Governor has some limitations:
- Complex Design: Compared to simple centrifugal governors, the Hartnell Governor has more moving parts, increasing complexity.
- Higher Maintenance: The spring mechanism requires regular maintenance and may wear out over time.
- Not Suitable for Very Low Speeds: Due to its spring mechanism, it is less effective for very low-speed applications.
- More Expensive: Manufacturing costs are higher due to additional components like springs and adjustable collars.
- Limited Load Variation Handling: While better than other governors, excessive sudden load variations may still affect stability.
Conclusion
The Hartnell Governor is a highly efficient, spring-loaded governor that provides quick response, better stability, and high-speed regulation. Unlike traditional centrifugal governors, it uses a spring mechanism to balance centrifugal force, making it ideal for high-speed engines.
