Fixed assets are permanent and long-term assets sources of a firm which are being used for carrying out the business operations.

Nature of Fixed Assets
Fixed assets are permanent in nature. The characteristics of fixed assets includes,
- They are physical and tangible in nature.
- Fixed assets are owned and are meant for performing a firm’s day-to-day activities.
- Fixed assets are not meant for sale as a part and parcel of their daily activities.
- Fixed assets accounts for a major part of firm’s total assets and require a substantial part of investment to acquire them.
Importance/Significance of Fixed Assets
Fixed assets acts as the major and primary facilities of a firm in order to perform the business operations. They play a vital role in a firm. without which the business activities cannot be carried out. Fixed assets are classified into different types on the basis of their importance in the firm. They are very significant and plays a crucial role in measurement, evaluation and presentation of the firm’s performance and it’s financial position. It is quite essential necessary to determine the expenditure that have incurred on fixed asset as it holds a considerable effect on the firm’s operations.
A firm‘s main objective behind investing in fixed assets is.
- To expand the firm’s operations in order to meet the market demand.
- To cope up with the advanced technology in the industry to reduce costs. increase quality of operations and to gain competitive advantage.
- To offer provide secondary business requirements like warehouses. distribution centres and so on. Thus, it is quite clear that the fixed assets forms the core facilities of a firm and plays a crucial role in the successful accomplishment of the firm’s objectives.
Determination of Value of Fixed Assets
The following are the principles and procedure for the determination of value of fixed assets,
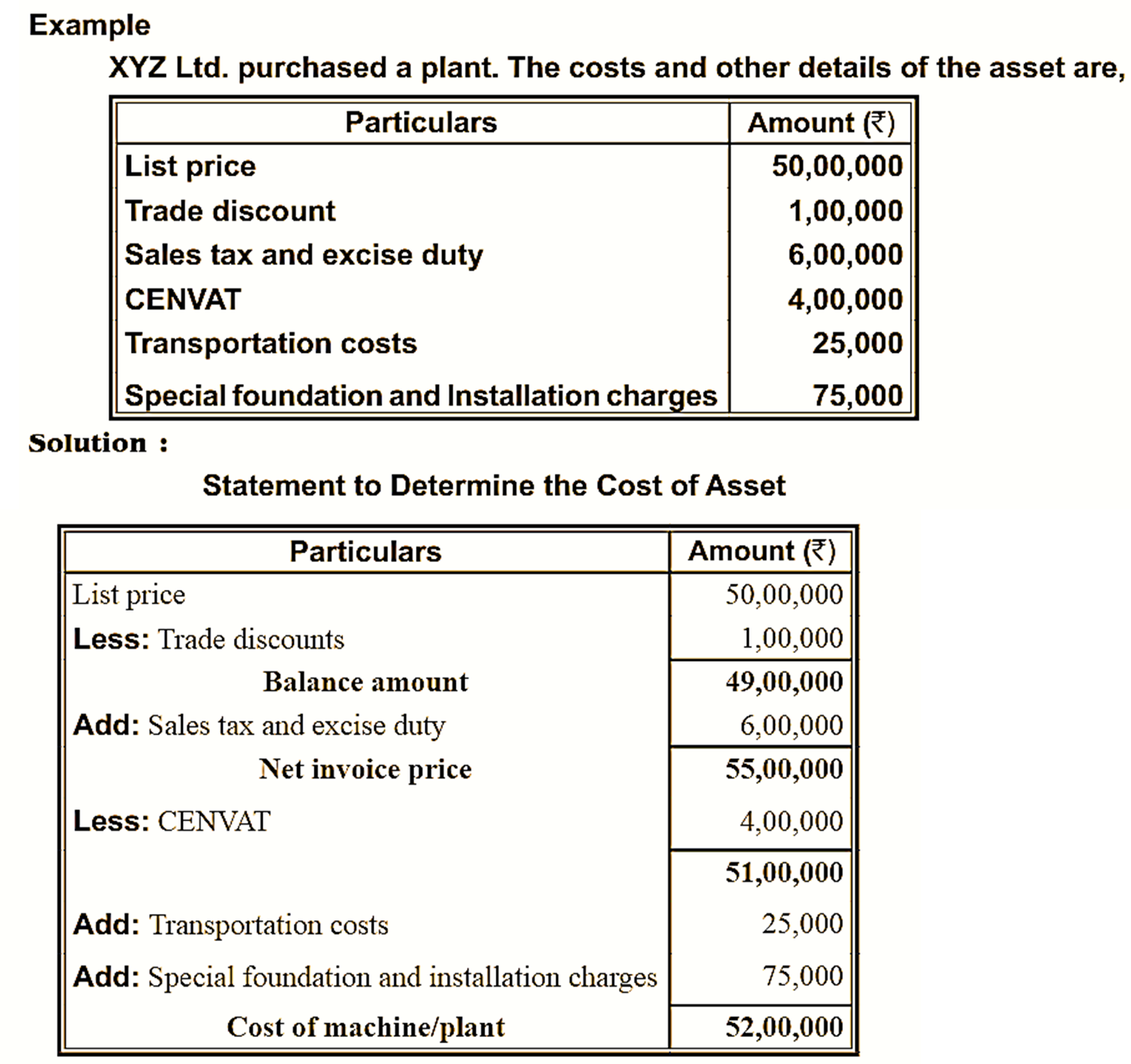
- The cost of fixed assets include purchase price, trade discounts, import duties and non-refundable taxes, direct costs associated with the assets such as installation costs, delivery costs etc.,
- While determining value of fixed assets, one should consider the changes in the prices and exchange rates as they have substantial effect on the value of fixed assets.
- The administration and other general overhead expenses that are associated with the project construction such as start-up costs, commission, experimental production costs.
- While determining the value/cost of self-constructed fixed assets and outsourced fixed assets. one should consider the direct costs associated with assets and construction of general assets for the functioning of special asset.
- For an asset that is exchanged for acquiring another one, the cost can be determined based on fair market value or net book value with reference to either of the exchanged asset. It should be adjusted with associated payments and receipts.
- For the cost of fixed assets one should add additional expenses associated with it which can generate high profits in future.
Revaluation of Fixed Assets
Sometimes the historical costs of financial statements can be replaced by the fixed assets costs. These revalued amounts will form basis for the calculation of depreciation on these assets. The guidelines for the revaluation accounting are.
- The book value of different categories of fixed assets can be determined based on different valuation criteria. The valuation methods include indexation with price indices and reference to current prices. The revaluated fixed assets should be continuously assessed using appraisal by competent valuer method.
- Net book value should be equal to net revalued amount. For which, firms need to restate the gross book value and accumulated depreciation along with the revalued fixed asset value.
- Firm should revaluate the whole class/category of assets in a systematic way.
- If the net book value is hither than the recoverable amount of assets of a class then the revaluation of fixed assets of that class does not yield their net book value.
- The rise in the net book value as a result of revaluation should be credited under revaluation reserves and it is not meant for allocation.
- The increased value can be credited under profit and loss account if it offsets the previous decline in net book value due to revaluation. Similarly, the decline in the net book value as a result of revaluation should be debited under profit and loss account.
