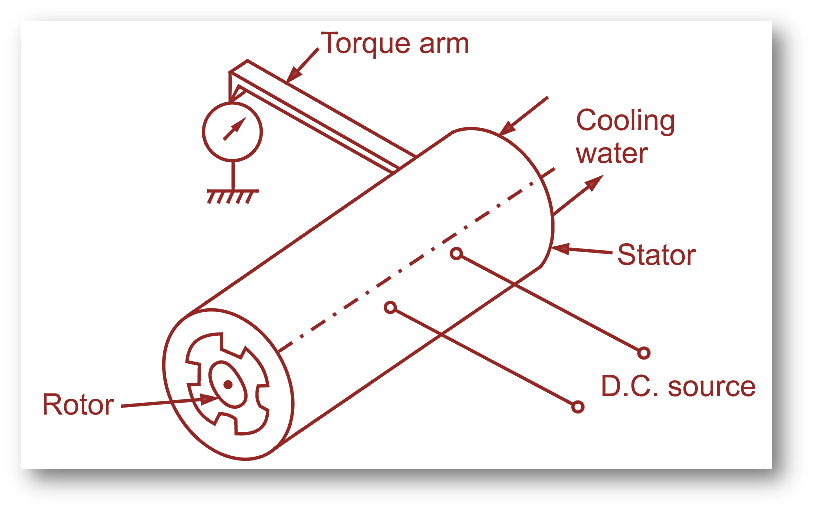
Fig. 1: Eddy current dynamometer.
Working Principle of Eddy Current Dynamometer
Eddy current dynamometer is electrical absorption dynamometer working on principle that, when isolated conductor moves through magnetic flux, it induces eddy current, which get dissipated in the form of heat.
Construction & Working of Eddy Current Dynamometer
It consists of toothed non-magnetic solid metallic rotor connected to the shaft whose power is to be measured. The non-magnetic rotor rotates inside smooth cast iron stator.
The stator is provided with exciting coil of D.C. source. The stator is mounted such that it permits free swing about its axis (Cradled) provided with torque arm, which measures torque.
To dissipate the generated heat, water is supplied in stator casing. During operation of dynamometer, rotor turns and causes constant change in flux density at all points of stator, resulting formation of eddy current, which opposes the motion of rotor. This opposing resistance is measured by brake drum in the form of torque, from which shaft power can be calculated.
Advantages of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- It can measure high power output at all speeds therefore it is used to test automobile and aircraft engines.
- It is compact as compared to other dynamometer of same capacity.
- The torque developed is smooth and continuous under all operating conditions.
- The absorption power can be changed by changing D.C. current.
Disadvantages of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- It can not produce any torque at zero speed.
- It produces small torque at low speed.
Applications of Eddy Current Dynamometer
- It can measure power upto 300 HP with maximum speed 6000 rpm.
