A domestic refrigerator is an electrical appliance used for preserving food and beverages at low temperatures. It uses a refrigeration cycle to remove heat from the stored items and maintain a controlled temperature, typically between 0°C and 4°C in the refrigerator compartment and around -18°C in the freezer.
Working Principle of a Domestic Refrigerator
A domestic refrigerator operates on the vapor compression refrigeration cycle, which consists of the following steps:
- Compression: The compressor compresses the low-pressure refrigerant gas into a high-pressure, high-temperature gas.
- Condensation: The high-pressure gas moves to the condenser tubes at the back of the refrigerator, where it dissipates heat and condenses into a high-pressure liquid.
- Expansion: The high-pressure liquid passes through the capillary tube, which causes it to expand and become a low-pressure, low-temperature liquid.
- Evaporation: The low-pressure liquid absorbs heat from the freezer and refrigerator compartments, cooling them down. The refrigerant evaporates back into a low-pressure gas and returns to the compressor to repeat the cycle.
Parts of a Domestic Refrigerator
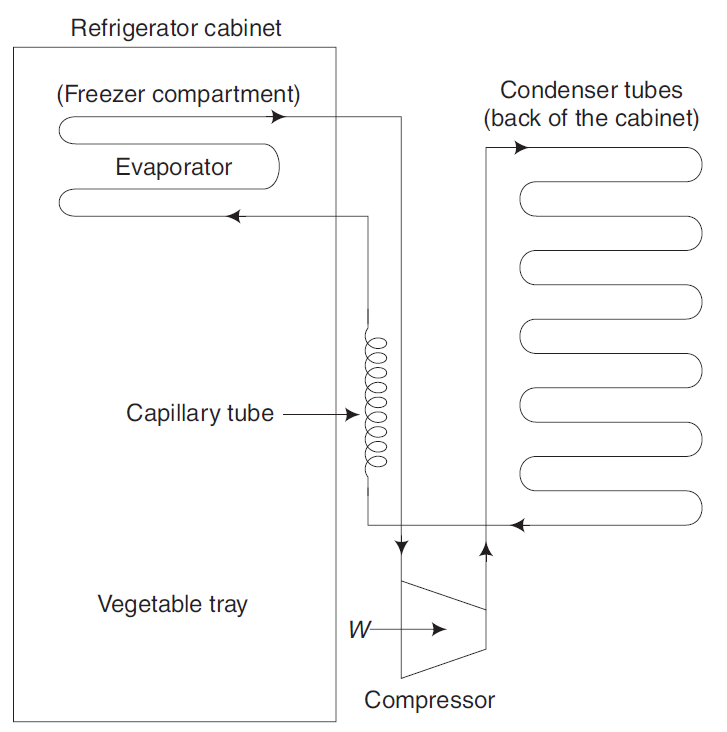
- Compressor: Located at the bottom rear, it compresses and circulates the refrigerant through the system.
- Condenser Tubes: Positioned at the back of the refrigerator, they release absorbed heat to the surrounding air.
- Capillary Tube: A thin tube that reduces the pressure of the refrigerant before entering the evaporator.
- Evaporator: Located inside the freezer compartment, it absorbs heat from the interior, cooling the air.
- Thermostat: Regulates the temperature by controlling the compressor operation.
- Refrigerator Cabinet: Insulated storage compartments for food and beverages.
- Vegetable Tray: Designed for storing vegetables and fruits at optimal humidity.
- Refrigerant: The working fluid that circulates through the refrigeration cycle.
- Defrosting System: Prevents excessive frost buildup inside the freezer compartment.
Types of Domestic Refrigerators
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Single Door Refrigerator | Compact and energy-efficient, suitable for small families. |
| Double Door Refrigerator | Features separate freezer and refrigerator compartments, offering more storage space. |
| Side-by-Side Refrigerator | Large capacity with side-by-side freezer and refrigerator sections, ideal for bigger families. |
| French Door Refrigerator | A combination of bottom freezer and double-door refrigerator, providing easy access and spacious design. |
| Mini Refrigerator | Small and portable, commonly used in offices, bedrooms, and hotels. |
| Bottom Freezer Refrigerator | Freezer compartment located at the bottom, allowing easy access to refrigerated items. |
| Top Freezer Refrigerator | Traditional design with a freezer on top and refrigerator below, widely used in households. |
Advantages of a Domestic Refrigerator
- Preserves Food Freshness – Prevents food spoilage by maintaining low temperatures.
- Energy Efficient – Modern refrigerators consume less electricity.
- Compact and Convenient – Designed for household use with multiple compartments.
- Temperature Control – Adjustable settings for different cooling needs.
- Multi-Functionality – Some models include features like fast freezing and moisture control.
Applications of a Domestic Refrigerator
- Households – Used for food and beverage storage.
- Hotels & Restaurants – Essential for preserving ingredients and beverages.
- Medical Facilities – Used to store medicines and vaccines.
- Laboratories – Helps in preserving biological samples and chemicals.
- Grocery Stores – Keeps perishable goods fresh for sale.
Disadvantages of a Domestic Refrigerator
- High Initial Cost – Advanced models can be expensive.
- Electricity Consumption – Requires continuous power supply.
- Maintenance Requirements – Needs periodic cleaning and servicing.
- Limited Storage Capacity – Not suitable for large-scale storage.
- Environmental Concerns – Refrigerants can contribute to ozone depletion if not handled properly.
Conclusion
A domestic refrigerator is an essential appliance for food preservation and storage. It operates using a vapor compression cycle, efficiently maintaining low temperatures. While it has numerous benefits, including energy efficiency and convenience, it also comes with limitations such as electricity consumption and maintenance requirements. Selecting the right refrigerator depends on factors like capacity, energy rating, and additional features based on user needs.
