The core marketing concepts involve, needs, wants and demands, marketing offers (products, services and experiences), value, satisfaction, exchanges, transactions, relationships and markets. There is a close link between all the core marketing concepts, which can be clearly explained with the help of the following figure,
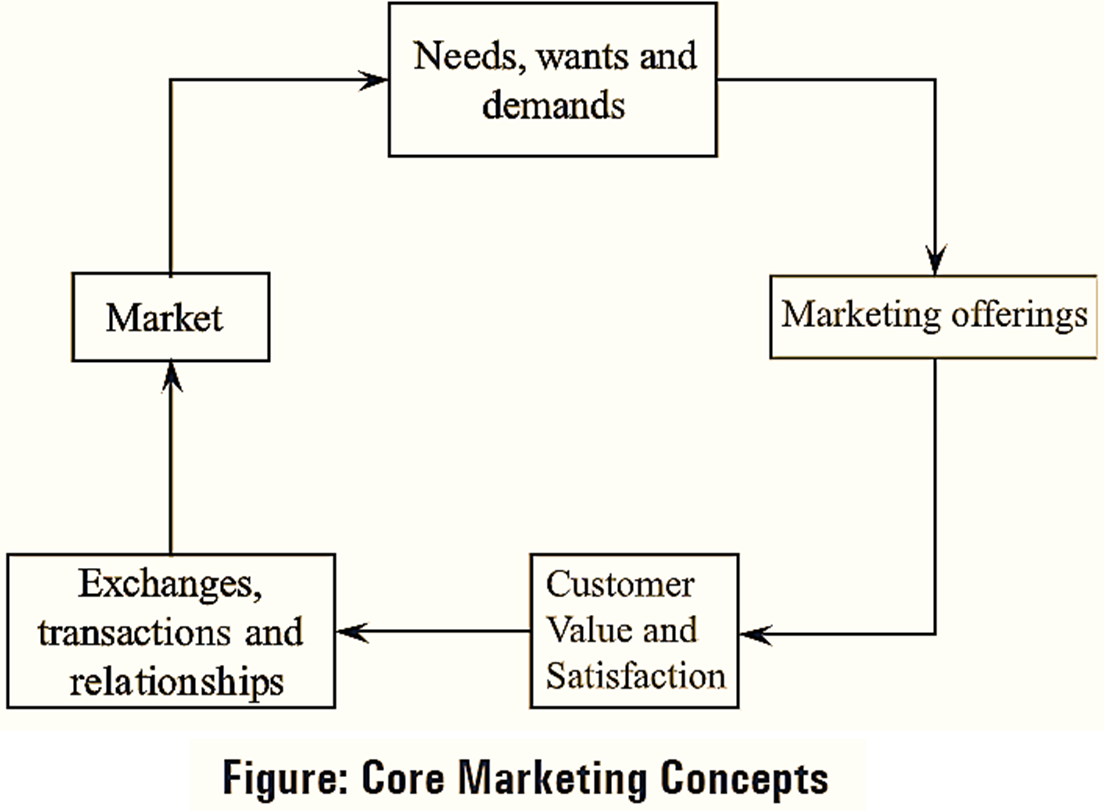
1. Needs, Wants and Demands
A human need is a state of felt deprivation of some basic satisfaction. Basic needs include the need for food, clothing and shelter. The needs are not created by a marketer as they are the inseparable part of human biology. During the course of time, a person may develop need for recreation, education etc. Wants constitute the specific forms of human needs. They are designed based on cultural and individual personality characteristics. Wants are mainly influenced by the society in which an individual survives. The only difference which is found between needs and wants is that human needs are limited while wants are unlimited. Demands are wants for any product or a service that are supported by an ability and willingness to purchase it. While estimating the demand for a product, firm (or a marketer) needs to consider both the preferences as well as the willingness/ability of a buyer to purchase it.
2. Market Offerings
Market offerings refer to the collection of products, services, information or experiences that can be offered to a market to satisfy a need, or a want. A core set of benefits that can be offered to customers for satisfying their needs which a marketer has promised is usually referred to as “value proposition”.
The major part of market offerings involve physical products which consists of non-durable goods and consumer durables. Some examples of non-durables are cosmetics like lipstick, toothpaste, shampoo, tea, coffee, chocolates, etc. Some examples of durables are automobiles electronics furniture etc.,
Marketing offers not only include physical products but also the intangible products like services, activities or benefits. Example of services are hotel, banking, tourism and travel etc.
3. Customer Value and Satisfaction
Every customer selects products and services based on his/her perceptions and satisfaction about the firm’s offerings. Basically customer satisfaction depends on the firm’s ability to effectively fulfill the expectations of customers. Customer value is denoted as,
Customer value = Benefits of customers obtained from his purchases – Cost of products
4. Exchanges, Transactions and Relationships
Exchange is one of the important concepts of marketing which is a process of obtaining an object by offering another in return. An exchange process involves two or more people, who possess the products/services who carry a certain value to the other. The process wherein somebody offers something and discusses the mutual benefits and acceptable terms for both the parties is usually referred to as “exchange”. A transaction takes place when two or more parties agree upon certain terms and conditions. A transaction includes the value exchange among two or more parties and even the shifting of ownership from the seller to the buyer. Marketing does not restrict itself to a single transaction which occurs between the marketer and the customer, but try to maintain a long term relationship with their customers by optimally satisfying their needs. The objective of marketers is not only to attract new customers and create transactions but also to maintain customers and improve their business with the company.
5. Market
A market is considered as a physical setting where buyers and sellers interact with each other for the exchange of goods. The sellers, marketers, competitors, buyers, regulator etc., are part of a market. Ex: Mobile market.
