Cogeneration, also known as Combined Heat and Power (CHP), is a process that simultaneously produces electricity and useful thermal energy from a single fuel source. It enhances overall efficiency by utilizing waste heat for heating, cooling, or industrial processes, reducing energy losses compared to conventional power generation.
Parts of a Cogeneration System
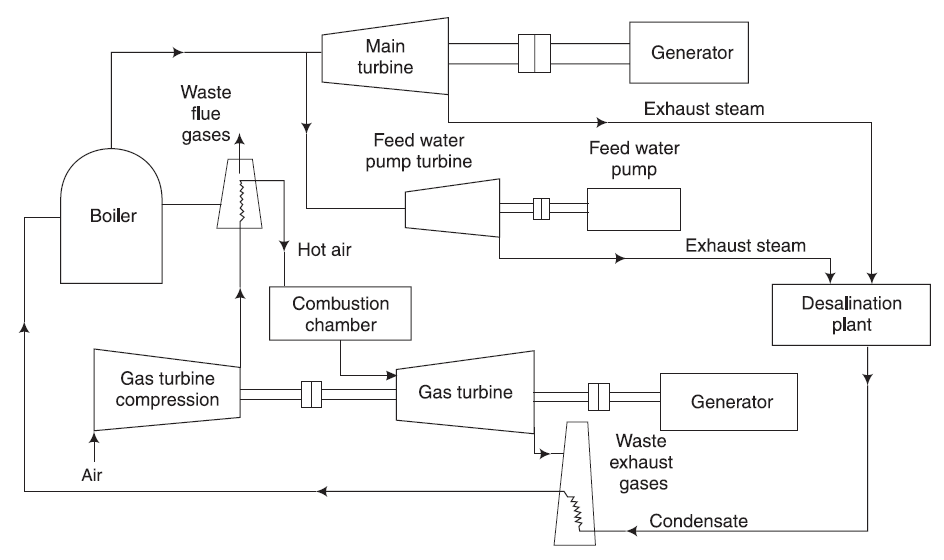
- Prime Mover (Gas or Steam Turbine, Reciprocating Engine): Converts fuel into mechanical energy to drive a generator.
- Generator: Produces electricity from the mechanical energy of the turbine or engine.
- Boiler: Produces steam by utilizing waste heat from the process.
- Combustion Chamber: Burns fuel to produce high-temperature gases for energy conversion.
- Heat Recovery Steam Generator (HRSG): Captures and repurposes waste heat for secondary applications.
- Feed Water Pump & Turbine: Maintains water circulation and pressure for steam generation.
- Cooling System: Helps in maintaining optimum operating temperatures.
- Exhaust System: Releases waste gases after energy extraction.
- Desalination Plant (Optional): Utilizes waste heat for freshwater production from seawater.
Working Principle of Cogeneration
The cogeneration system integrates power generation and thermal energy utilization within a single process. It typically consists of a prime mover (such as a gas turbine, steam turbine, or reciprocating engine), a generator, and a heat recovery system. The fuel (natural gas, biomass, coal, or waste fuels) powers the turbine or engine, generating electricity. Instead of discarding the excess heat, it is recovered through a heat exchanger and utilized for heating, desalination, or industrial applications.
Types of Cogeneration
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Steam Turbine Cogeneration | Uses steam turbines to generate electricity and capture waste heat for other uses. |
| Gas Turbine Cogeneration | Employs gas turbines to produce electricity and utilize exhaust gases for heating. |
| Combined Cycle Cogeneration | Integrates gas and steam turbines for improved efficiency and maximum energy recovery. |
| Reciprocating Engine Cogeneration | Uses internal combustion engines to generate power and recover heat from exhaust gases. |
| Fuel Cell Cogeneration | Employs fuel cells to produce electricity and use byproduct heat efficiently. |
Advantages of Cogeneration
- Higher Efficiency: Utilizes fuel more efficiently compared to conventional power plants.
- Reduced Energy Costs: Saves costs by providing both electricity and thermal energy.
- Lower Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Reduces CO2 emissions due to improved fuel efficiency.
- Reliability: Provides stable and continuous energy supply.
- Fuel Flexibility: Can operate using various fuels, including natural gas, biomass, and coal.
- Waste Heat Utilization: Enhances energy conservation by repurposing thermal energy.
Applications of Cogeneration
- Industrial Facilities: Used in industries requiring both power and heat, such as chemical plants and refineries.
- District Heating: Provides heating and electricity to residential and commercial areas.
- Desalination Plants: Used for water desalination using waste heat.
- Hospitals & Universities: Ensures reliable energy supply for large institutions.
- Greenhouses & Food Processing Units: Utilized for heating and energy needs in agricultural and food industries.
- Waste Treatment Plants: Used for waste-to-energy conversion and biogas utilization.
Disadvantages of Cogeneration
- High Initial Investment: Requires significant capital for equipment and installation.
- Complex System Design: Needs careful planning and engineering for effective integration.
- Maintenance Requirements: Regular upkeep is necessary to maintain efficiency.
- Site Dependency: May not be suitable for all locations due to fuel and space constraints.
- Limited Load Flexibility: Best suited for applications with consistent heat and power demands.
Cogeneration is a highly efficient and sustainable energy solution, widely adopted in various sectors for reducing energy waste and lowering operational costs while enhancing environmental sustainability.
