A bomb calorimeter is a scientific instrument used to measure the heat of combustion of a substance. It operates under constant volume conditions and is commonly used in thermodynamic studies, food science, and fuel analysis. The device consists of a strong, sealed container called a bomb, in which the sample is burned in an oxygen-rich atmosphere to determine its energy content.
Parts of a Bomb Calorimeter
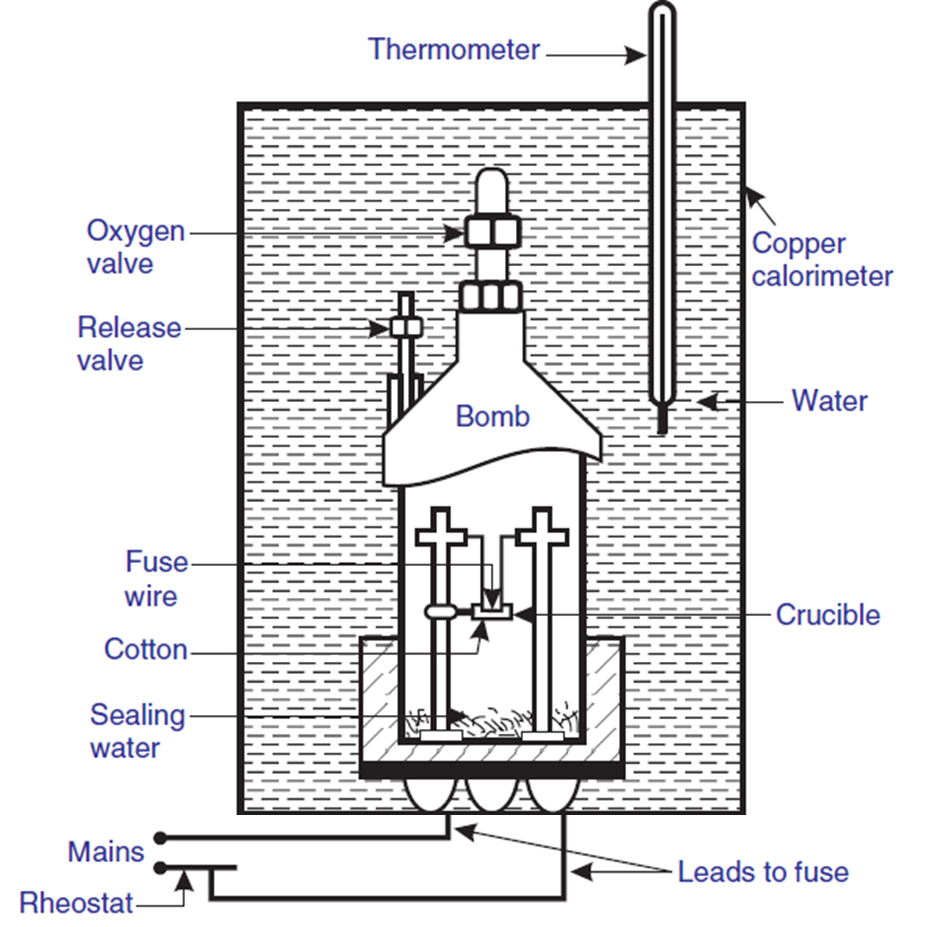
- Bomb – A strong, sealed steel container that holds the sample and oxygen.
- Crucible – A small dish where the sample is placed for combustion.
- Oxygen Valve – Supplies pure oxygen to ensure complete combustion.
- Fuse Wire – Ignites the sample using an electric current.
- Cotton – Helps in complete combustion by ensuring proper ignition.
- Sealing Water – Prevents heat loss and maintains pressure balance.
- Copper Calorimeter – Surrounds the bomb and holds the water that absorbs the released heat.
- Water – Absorbs the heat released by combustion.
- Thermometer – Measures the temperature change in water.
- Rheostat & Mains – Provide electrical power to ignite the fuse wire.
Working Principle of a Bomb Calorimeter
The working of a bomb calorimeter is based on the first law of thermodynamics (conservation of energy) and operates under constant volume conditions. The energy released during combustion is absorbed by the surrounding water, and the change in water temperature is used to calculate the calorific value of the sample.
Steps in Working
- A known mass of the sample is placed in the crucible inside the bomb.
- The bomb is filled with pure oxygen under high pressure.
- The bomb is sealed and placed in a copper calorimeter filled with a known amount of water.
- A thermometer is inserted to measure the initial temperature of the water.
- The sample is ignited using an electric fuse wire, which initiates combustion.
- The heat released by combustion is transferred to the surrounding water.
- The final temperature of the water is recorded.
Advantages of Bomb Calorimeter
- Accurate Measurement: Provides precise heat of combustion values.
- High Efficiency: Ensures complete combustion under controlled conditions.
- Reproducibility: Produces consistent results for reliable analysis.
- Broad Application: Used in fuel, food, and chemical industries.
- Controlled Environment: Oxygen-rich atmosphere allows complete combustion.
Applications of Bomb Calorimeter
- Fuel Industry: Determines the calorific value of coal, gasoline, and biofuels.
- Food Science: Measures the energy content of food items.
- Pharmaceuticals: Evaluates the energy release of chemical compounds.
- Environmental Studies: Helps in studying waste management and combustion properties.
- Research and Development: Used in various thermodynamic experiments.
Disadvantages of Bomb Calorimeter
- Expensive Equipment: High initial cost.
- Complex Setup: Requires precise calibration and maintenance.
- Time-Consuming Process: Each experiment takes considerable time.
- Safety Concerns: High-pressure oxygen can pose explosion risks.
- Limited to Combustible Samples: Cannot measure energy of non-combustible substances.
Conclusion
The bomb calorimeter is a crucial tool for measuring the heat of combustion of various substances. Its accuracy and reliability make it indispensable in energy-related research, industry, and academia. Despite some disadvantages, its benefits outweigh the limitations, making it a fundamental instrument in calorimetric studies.
