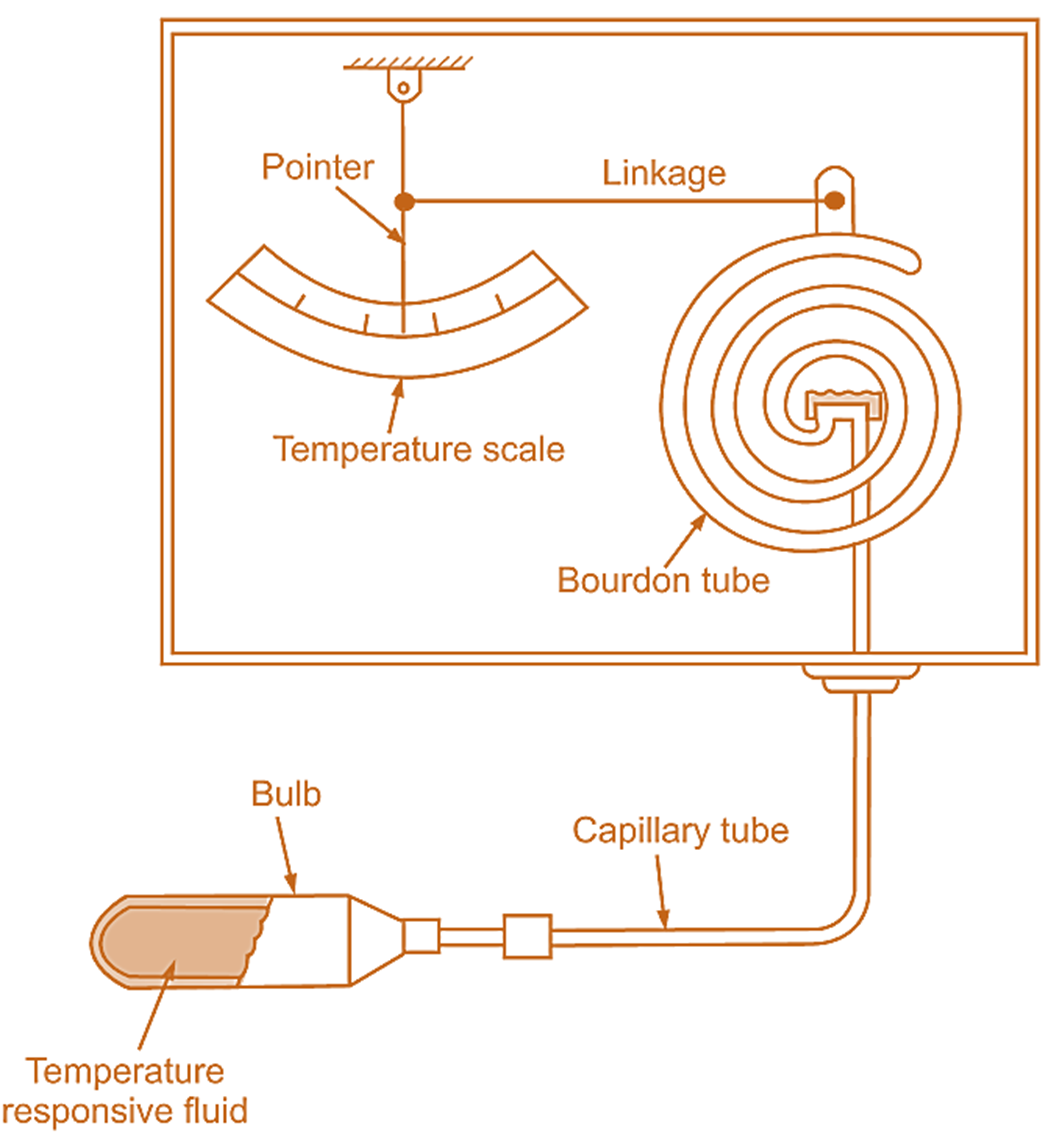
Figure 1: Pressure Thermometer.
Construction & Working of Pressure Thermometer
The operation of pressure gauge thermometer is based upon the expansion of liquid, gas or vapour in the bulb of the thermometer. It consists of bulb containing a liquid, gas or vapour, which is immersed in environment. The bulb is connected by capillary tube to some pressure measuring device, this pressure measured is calibrated to indicate temperature.
Pressure Bulb or Sensor:
The sensing element is pressure bulb, which contains a thermometer fluid and is placed where temperature is measured. The bulb is made of cylindrical piece of metal tubing closed at one end and connected to capillary tubing at the other end. The size of bulb used depends upon the type of fluid used, temperature span of system and the length of capilary tube used with it.
Capillary Tube:
A capillary tube is used to connect the bulb with pressure measuring device. The length of capillary tube is made as short as possible in order to improve dynamic performance. The capillary tube is made of copper or steel for systems using fluids other than mercury. When mercury is used as the transmitting fluid, stainless steel capillary tube is used.
Pressure Measuring Device:
The pressure measuring device may be bourdon tube, diaphragm, or bellow. The displacement of this is amplified to operate a pointer over a stationary scale. The scale may be calibrated to give temperature.
Advantages of Pressure Thermometer:
- They are most economical and versatile for the measurement of temperature.
- They are rugged in construction and have little chance of damage.
- Remote indication upto 60 m is possible.
- Accuracy is ± 1%.
