An Induced Draught Cooling Tower is a type of cooling tower where an induced draught fan is placed at the top of the tower to pull air through the system. This improves heat exchange efficiency and ensures uniform airflow across the cooling media. These towers are widely used in industries like power generation, HVAC systems, and chemical plants.
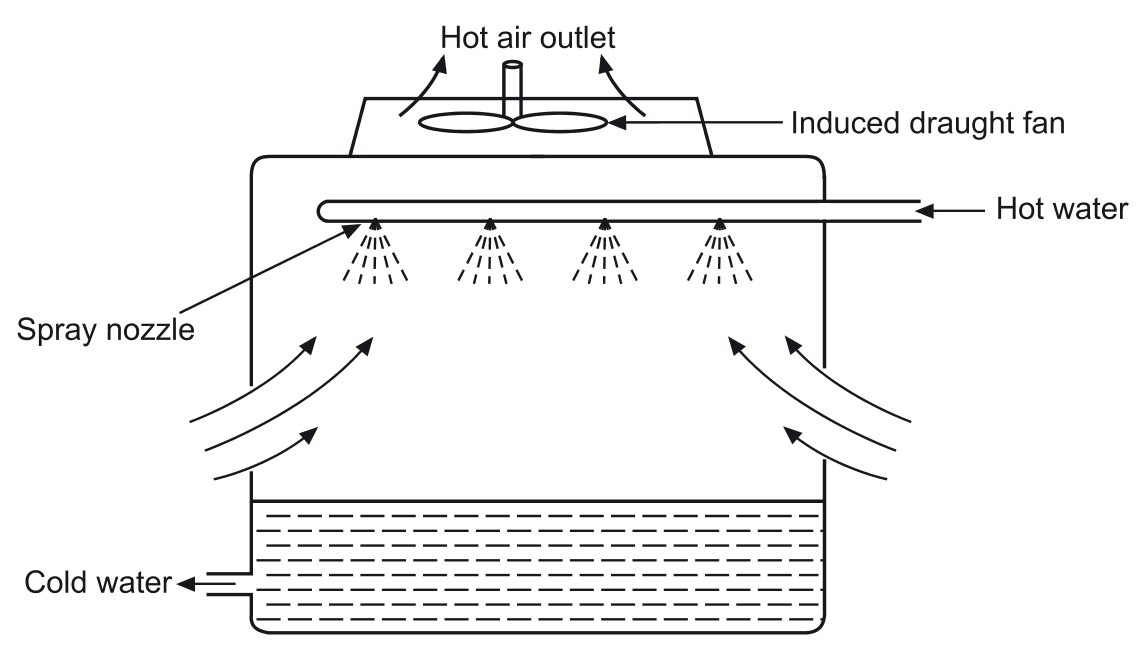
Working Principle of an Induced Draught Cooling Tower
An induced draught cooling tower works by utilizing a fan at the top to pull air through the system, thereby enhancing heat dissipation. The process follows these steps:
- Hot water enters the cooling tower through an inlet pipe.
- The hot water is distributed via spray nozzles, forming small droplets.
- Air enters the tower from the sides at the bottom due to the suction effect created by the induced draught fan at the top.
- The air moves upward, interacting with the falling water droplets, causing evaporation and cooling.
- The cooled water is collected at the bottom and exits through the cold water outlet.
- The warm, moist air is expelled through the hot air outlet at the top, ensuring a continuous cooling cycle.
Parts of an Induced Draught Cooling Tower
- Hot Water Inlet – Delivers heated water from the industrial process.
- Spray Nozzles – Disperse water into fine droplets for enhanced heat transfer.
- Air Inlet – Allows fresh air to enter the cooling tower.
- Cooling Media (Fill Material) – Enhances contact between water and air.
- Cold Water Basin – Collects cooled water at the bottom of the tower.
- Induced Draught Fan – Located at the top, it pulls air through the system.
- Hot Air Outlet – Expels warm, humid air after heat exchange.
Advantages of Induced Draught Cooling Towers
- Higher Efficiency – Enhanced cooling due to better airflow control.
- Lower Power Consumption – More efficient than forced draught towers.
- Better Water Distribution – Ensures effective heat exchange.
- Compact Size – Requires less space compared to natural draught towers.
- Less Affected by Wind Variations – Consistent performance under different weather conditions.
Applications of Induced Draught Cooling Towers
- Power Plants – Used for cooling condenser water in thermal plants.
- HVAC Systems – Applied in large air conditioning and refrigeration systems.
- Chemical & Petrochemical Plants – Used in process cooling.
- Steel & Manufacturing Industries – Helps in temperature regulation.
- Food & Beverage Industry – Maintains cooling during food processing.
Disadvantages of Induced Draught Cooling Towers
- Higher Initial Cost – Requires investment in mechanical components.
- Maintenance Requirements – Fans and motors need periodic servicing.
- Noise Generation – Induced draught fans can be noisy.
- Risk of Corrosion – Exposure to moisture may lead to material degradation.
- Drift Losses – Some water can be lost as mist if not properly managed.
