A slotter machine is a type of machine tool that is primarily used for cutting slots, grooves, and keyways into materials like metals and plastics. It operates by moving a single-point cutting tool vertically and intermittently against the workpiece, which is usually fixed to a table. Slotter machines are versatile tools often used in manufacturing, machining, and repair workshops.
What is Slotter Machine?
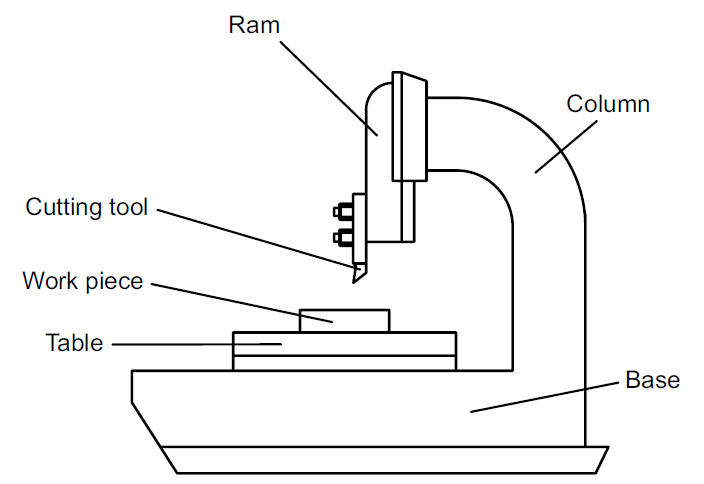
Figure 1.
A slotter machine is a mechanical device designed to cut precise vertical slots or grooves in various materials. It operates with a reciprocating motion of the cutting tool to achieve the desired shape or profile on the workpiece. Slotter machines are similar to shapers but are specialized for vertical or angular cutting.
Parts of a Slotter Machine
The primary components of a slotter machine are:
- Base: The base is the foundation of the slotter machine, providing stability and support to the entire structure. It absorbs vibrations during operation to ensure precision.
- Column: The column is a vertical structure attached to the base. It houses the ram and other mechanisms, offering rigidity and guiding the ram’s motion.
- Ram: The ram is the part that holds and moves the cutting tool in a vertical reciprocating motion. It is driven by mechanical or hydraulic means.
- Cutting Tool: The cutting tool is a single-point tool used to perform the cutting operation. It is made of high-speed steel (HSS) or carbide materials for durability and precision.
- Table: The table holds the workpiece in place. It can be rotated or moved horizontally to position the workpiece correctly under the cutting tool.
- Workpiece Holder: A vice or clamps are used to secure the workpiece on the table during machining.
- Feed Mechanism: This mechanism allows the gradual movement of the workpiece or tool for consistent material removal.
- Cross Slide: The cross slide is used to adjust the table’s position in the horizontal direction.
- Driving Mechanism: It includes the motor, belts, pulleys, and gears responsible for transmitting power to the machine.
- Stroke Adjustment Mechanism: This component adjusts the length of the ram’s stroke to suit the cutting requirements.
Working Principle of a Slotter Machine
The slotter machine operates on the principle of converting rotary motion into reciprocating motion. The cutting tool, attached to the ram, moves in a vertical reciprocating motion while the workpiece remains stationary or moves slightly for feed adjustment. During the cutting stroke, the tool removes material from the workpiece, and in the return stroke, the tool lifts off the surface to prevent interference.
Steps:
- The workpiece is securely mounted on the table.
- The cutting tool is fixed in the ram and positioned appropriately.
- The stroke length and feed are adjusted based on the work requirements.
- The machine is started, and the ram moves vertically, allowing the cutting tool to remove material.
- The process continues until the desired slot or groove is achieved.
How a Slotter Machine Works
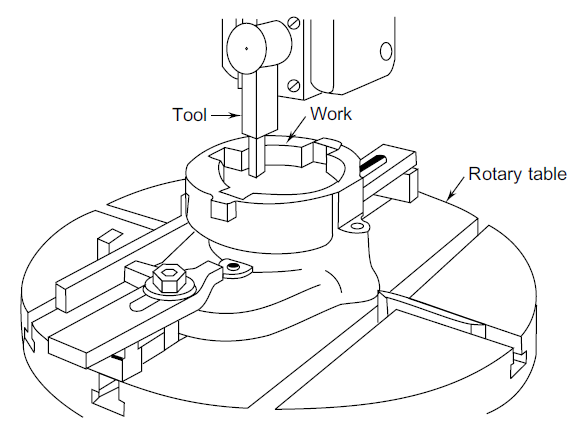
- Tool Movement: The cutting tool moves vertically in a reciprocating motion. The cutting stroke happens in the downward direction, while the return stroke is idle.
- Workpiece and Rotary Table: The workpiece is mounted on a rotary table, which allows for angular adjustments and precise positioning. The table can be rotated manually or automatically to cut keyways, slots, grooves, or internal profiles.
- Material Removal: The tool removes material during the downward stroke by shearing small chips. This process is suitable for internal keyways, spline cutting, and intricate shapes inside a workpiece.
Types of Slotter Machines
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Puncher Slotter Machine | Used for heavy-duty applications, designed for punching and cutting slots in large and heavy workpieces. |
| Precision Slotter Machine | Ideal for fine and accurate slotting operations, commonly used in toolmaking and die-making industries. |
| General Purpose Slotter Machine | Suitable for medium-duty tasks and versatile for general machining operations. |
| Hydraulic Slotter Machine | Operates using hydraulic power for smooth and efficient operation, capable of handling high loads with precision. |
| Vertical Slotter Machine | Designed for creating vertical slots or grooves and is the most commonly used type in workshops. |
Specifications of Slotter Machines
The following specifications define the capabilities of a slotter machine:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Stroke Length | 100 mm to 1200 mm |
| Table Diameter | Variable based on machine size |
| Maximum Workpiece Height | Depends on machine design |
| Number of Strokes per Minute | Adjustable speed settings |
| Motor Power | Varies by model |
| Feed Range | Longitudinal and cross feed options |
| Machine Weight | Depends on the size and design |
Advantages of Slotter Machines
- Versatility: Can cut slots, grooves, keyways, and internal profiles.
- Precision: Ensures accurate and consistent cutting.
- Simple Operation: Easy to operate and adjust.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable for medium-scale machining operations.
- Durable: Built to withstand heavy-duty operations.
Applications of Slotter Machines
Slotter machines are widely used in various industries, including:
- Automotive: Cutting keyways and slots in gears and shafts.
- Aerospace: Machining intricate parts with precision.
- Tool and Die Making: Creating dies, molds, and specialized tools.
- Construction: Slotting components for heavy machinery.
- Repair Shops: Refurbishing worn-out parts by adding new slots.
- Furniture Manufacturing: Cutting decorative grooves in wooden parts.
Disadvantages of Slotter Machines
- Slow Process: The reciprocating motion limits the speed of material removal.
- Limited Capability: Not suitable for large-scale or high-speed production.
- High Maintenance: Requires regular maintenance for optimal performance.
- Manual Intervention: Many operations require manual adjustments, increasing labor costs.
- Material Restrictions: Less effective on extremely hard materials compared to advanced CNC machines.
